Height8
26 September 2024
Expansion of Rural Broadband: Technology & Economy
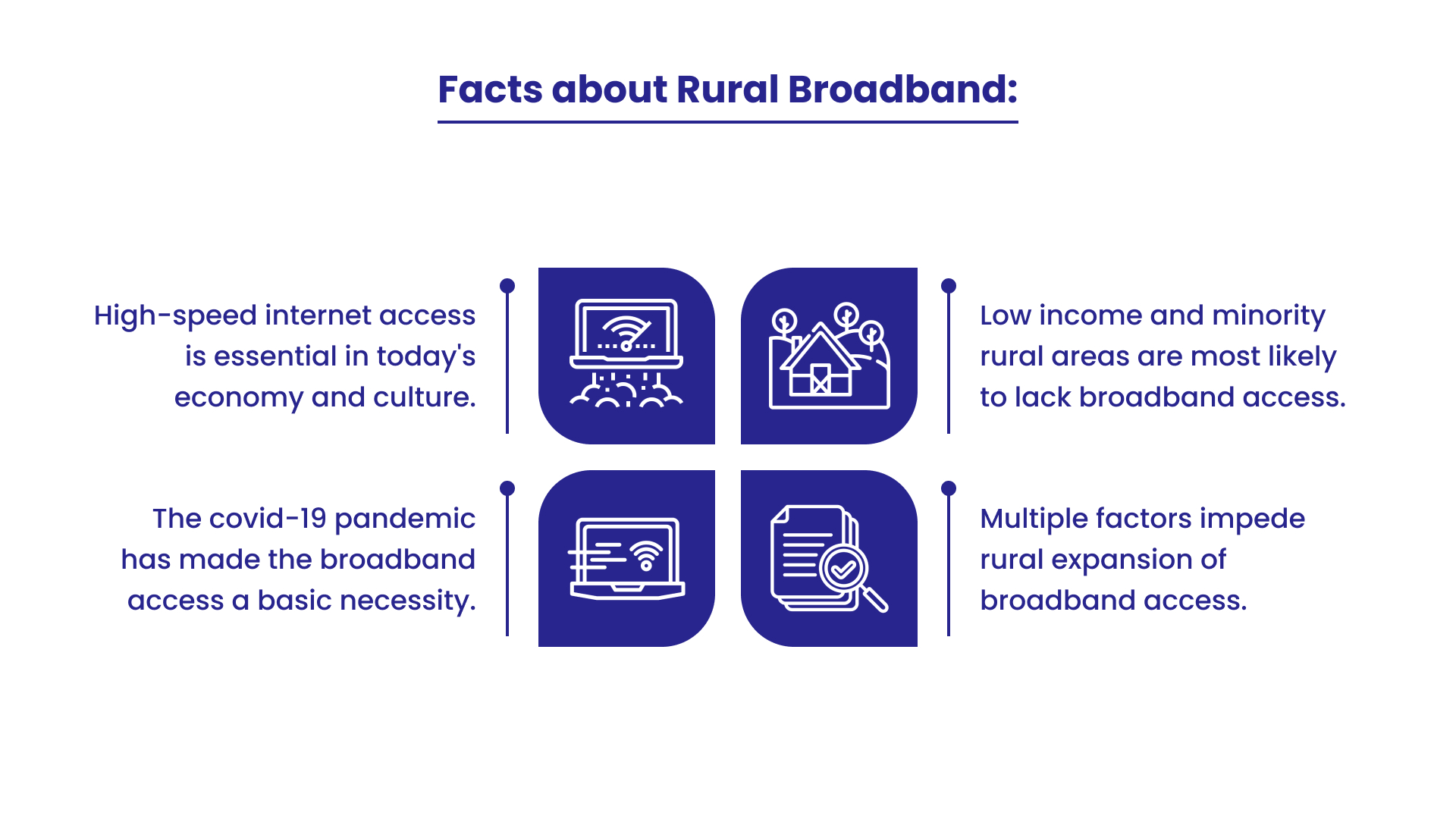
High-speed broadband internet service has become a necessity from a luxury good. There is usually poor broadband infrastructure coverage in the Rural area as they pose a costly business case for providers. Broadband access and adoption in rural areas are directly equivalent to increased job and population growth, higher rates of new business formation and home values, and lower unemployment rates.
Lack of access to the internet in rural areas is not a new problem. Low population density and long area distance is the real challenge for Internet Service Providers (ISPs) for providing broadband internet access in rural areas.
At the start of the pandemic, the Pew Research Center conducted a national survey that drives the importance of reliable internet service. At that time, the internet was a source of information about the coronavirus and a tool for connecting with doctors and other medical professionals for both urban and rural respondents: 62% of rural respondents searched online for coronavirus information, and 13% used the internet for communicating with health professionals. Along with this, 14% of rural respondents used the internet to work remotely.
But what are the challenges faced by ISPs in providing broadband in the rural areas of the USA? How can ISPs manage costs and deliver the best services in the rural areas of the USA? This blog has the answers to your questions.
Let’s proceed!
Challenges in Expansion of Rural Broadband
The first and foremost challenge is Technology. Fiber cables have to travel more distance which will increase the cost. Connecting a single household in a rural area costs around 5 to 6 thousand dollars which makes ISPs much more difficult. ISPs cannot afford to provide broadband internet which costs higher in rural areas.
Another challenge is the affordability of rolling out broadband. Wireless, sometimes, won’t work effectively because of the trees and farmsteads in the rural areas.
How Can ISPs Manage Cost and Deliver Best Services?
The internet has become a necessity after the pandemic as the dependency has increased either in the form of work from home or virtual learning school lectures. ISPs have to understand that the current and future build plans revolve around fiber and bringing robust access to customers while developing software capabilities will increase the user experience in today’s digital economy.
Huge subsidies will likely be needed to expand broadband in the rural areas of the United States. Also, technologies may be required in high-cost areas where rapid expansion is needed.
All the states have to come up with a broadband program because of the availability of broadband funds allotment through capital projects.
These funds can be put into a state broadband program. An initial round for each state is about US$100 million which will go into a state broadband program, which will be used to fund the Federal Communication Commission (FCC) mapping program. After this, each state will get the granted monies on a requirement basis. The main objective of these initiatives is to get fiber out to rural areas and get customers served by resilient and future-proof technology.
Summing Up
Yes, It can be costly to expand broadband in rural areas, but the potential payoff is high. The COVID-19 pandemic highlights the necessity of high-speed internet access for almost all Americans. Various factors make rural areas too expensive for internet service providers, subsidies play an important role in making rural areas economically feasible for service. Comparing the costs of expansion against the subsidies available today shows that more subsidies are needed to close the gap. Engaging electrical cooperatives, using alternative technologies, and, in some instances, public-private partnerships work best for getting the job done.
Have any questions? Write us a mail at h8ssrms@height8tech.com or call/WhatsApp us at +91-6358931775.
Follow us on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, and YouTube to get updates on the latest technological advancements in the telecom sector.