Height8
03 February 2021
Evolution Of Telecom Industry In India
We all are aware of the Telecom Industry and its significant contribution to the economic growth of India. But do we know how it evolved? How did we reach from 2G to 5G? How Indias Telecom Industry gained the 2nd position in the world? Certainly, only few are able to answer these questions. No worries! Be with us and you will get all the information about the evolution of the Telecom Industry in India at the end of this blog which hardly takes your 3-4 minutes.
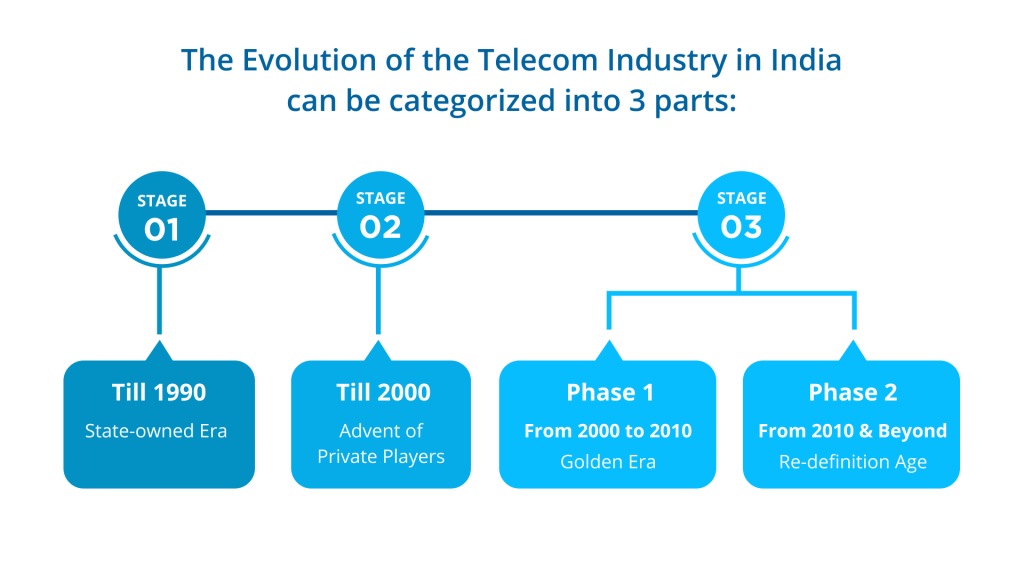
The Evolution of Telecom Industry in India can be categorized into 3 parts:
Stage 1 - Till 1990 - State-owned Era
Stage 2 - Till 2000 - Advent of Private Players
Stage 3 - Phase 1 - From 2000 to 2010 - Golden Era
Phase 2 - From 2010 & Beyond - Re-definition Age
Lets dig in!
Stage 1 - Till 1990 - State-owned Era
In the first stage, the telecom sector was owned and run by the government. The telephone services began in India with a manual telephone exchange in 1882 in kolkata.
The telecom industry evolved only after the Department of Telecommunication (DoT) was separated from the Indian post and telecommunication department in 1985. DoT was responsible for telecom services of the entire country till 1986. Subsequently, MTNL and VSNL were carved out of the Department of Telecommunication (DoT) for separation of its policy functions and telecom operations in metro cities like Mumbai and Delhi and International long distance operations.
This gives rise to the 2nd part of the telecom industry in India in which the government allows private players to enter the Telecom Industry.
Stage 2 - Till 2000 - Advent of Private Players
In 1994, the government introduced the National Telecom Policy (NTP) for private players. This policy clearly laid down the role of private operators. Cellular services were first launched in 1995 in Kolkata.
Another milestone during this Era was the formation of TRAI in 1997. TRAI was formed to regulate the fair environment between operators and subscribers.
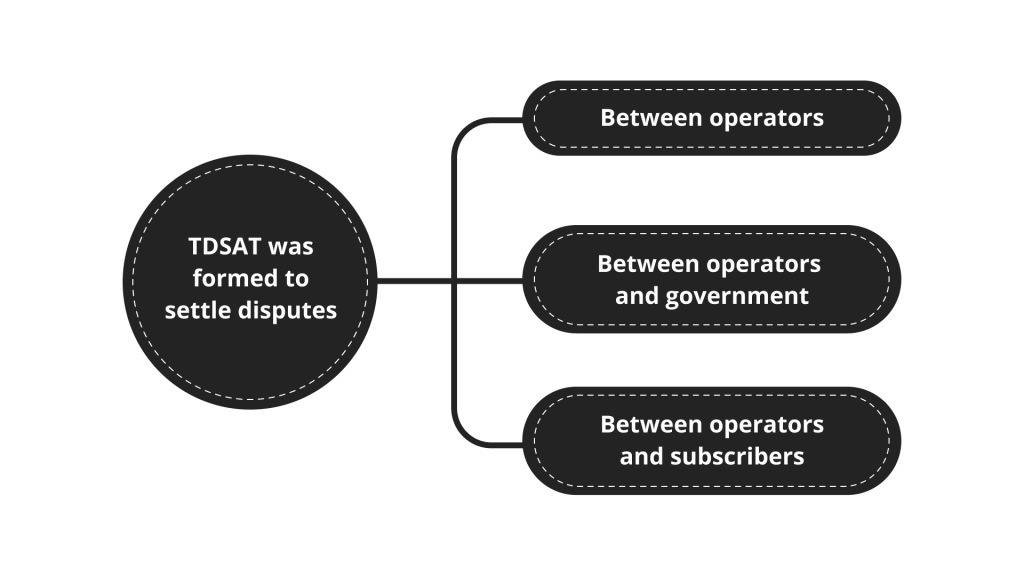
In 2000, the third organization called TDSAT was formed to settle the disputes between operators, between operators and government, and between operators and subscribers.
During this period telecom subscriptions were growing rapidly, Operators brought in new innovations like prepaid, this reduces the mobile fees and allows cell phones affordable to common men.
After march 2000, the government became more liberal and started issuing more licenses and reduced license fees. This starts the 3rd stage of the telecom industry.
Stage 3
The third stage of the telecom sector can be categorized into 2 parts. The first part from 2000 to 2010 telecommunication grew phenomenally is called the Golden Era. The second part from 2010 and beyond is called the Re-definition Age.
Stage 3 - Phase 1 - From 2000 to 2010 - Golden Era
In the golden Era, in 2005, 2G gave rise to mobile users. The number of mobile connections rapidly crosses the number of fixed-line connections.
Indian telecom market is one of the fastest growing and most competitive markets in the world. In the same year, the government increased the foreign Direct Investment (FDI) limit in the telecom sector from 49% to 74%.
Stage 3 - Phase 2 - From 2010 & Beyond - Re-definition Age
The most significant contributors of the Re-definition age are the introduction of 3G in 2008 and 4G in 2012. The introduction of 3G and 4G networks gives advent to the Smart Phones. This brought in mobile advertising, mobile commerce, video calling, streaming, full movie download, live TV, and multi-player gaming to everyones handset.
After 2G, 3G and 4G, the 5G is now all set to launch in India.
Conclusion:
The Telecom industry is growing at a rapid pace in India. It is one of the ever-growing industries in the world today. Today, Indias Telecom sector stands 2nd in the world in terms of market share. India is witnessing significant growth in terms of mobile subscriptions. It has contributed significantly to the economic growth of India.
Over the last decades, the Indian telecom sector has undergone a complete transformation. As in the future, one thing is for sure that the telecom sector will play a pivotal role in the Indian economy.